typeof operator in Javascript
4 min read
Do you actually know how to use typeof in Javascript?
Do you now what are typeof operator capabilities?
Well, we are going to explore typeof in depth.
typeof in Javascript
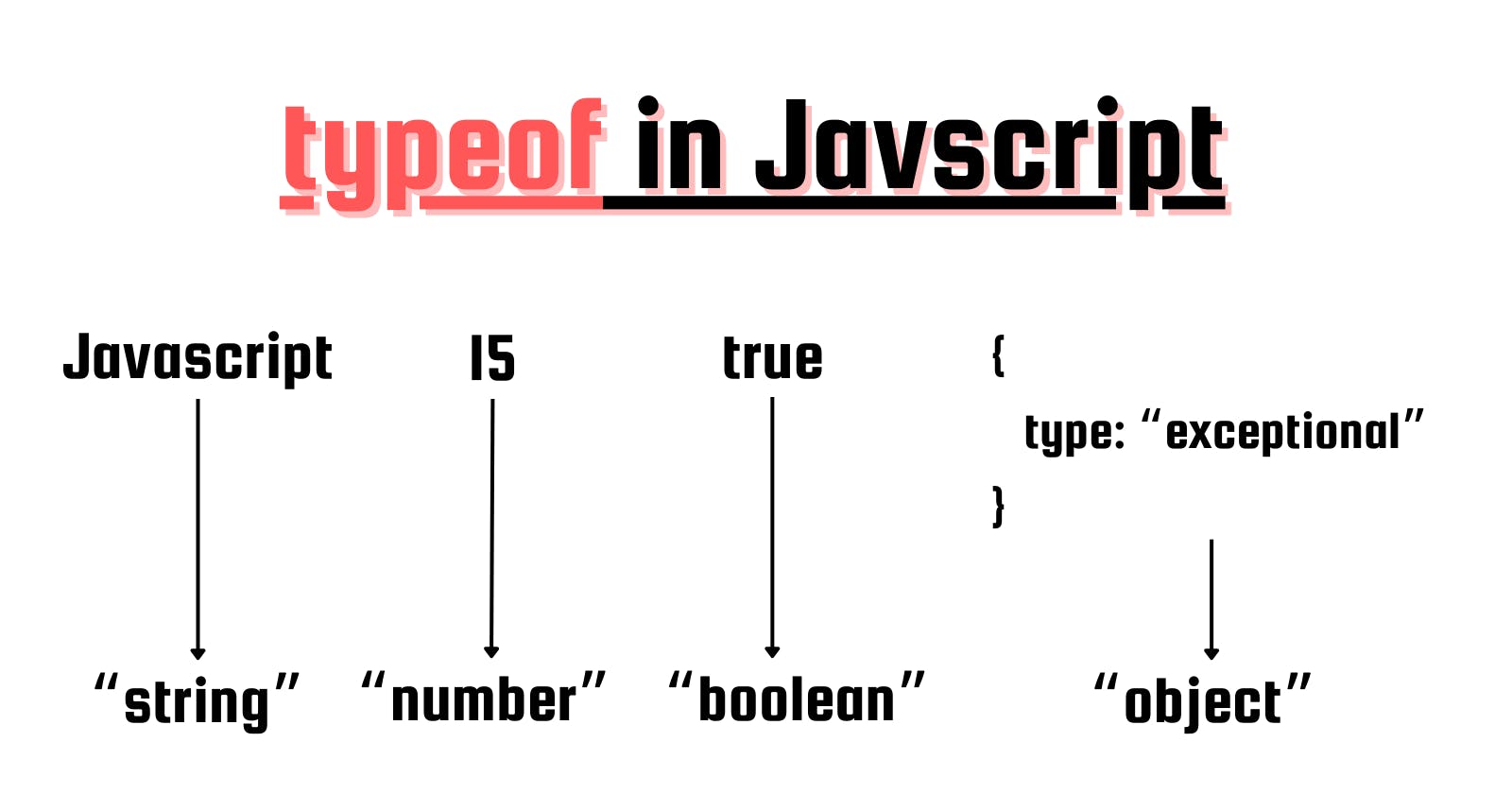
typeof is an operator which can be used to get the type of any operand. It will return a string which denotes the type. It can also be used in runtime to check the type.
It will return possible value from string, number, boolean, object, function, undefined, symbol and bigint
What typeof returns based on the value
Let start with an example. Let say you have a value and you want to know its type. Doesn't matter where this value(in this case myName and myAge which holds a string and number respectively ) comes from. It may come from an API or from an external library. Just for simplicity we are taking ourself into a variable.
let myName = "Sam";
let myNameType = typeof myName;
console.log(myNameType); // "string"
let myAge = 18;
let myAgeType = typeof myAge;
console.log(myAgeType); // "number"
It will return a string in case of myName and number in case of myAge.
Javascript will check the typeof value that you have provided and returns its type as:
let's create a Pseudocode for getting typeof value:
1. Let val be the result of evaluating UnaryExpression.
2. If val is a Reference Record, then
a. If IsUnresolvableReference(val) is true, return "undefined".
3. Set val to the result of GetValue(val).
4. If val is undefined, return "undefined".
5. If val is null, return "object".
6. If val is a String, return "string".
7. If val is a Symbol, return "symbol".
8. If val is a Boolean, return "boolean".
9. If val is a Number, return "number".
10. If val is a BigInt, return "bigint".
11. Assert: val is an Object.
12. NOTE: This step is replaced in section B.3.6.3.
13. If val has a [[Call]] internal slot, return "function".
14. Return "object".
Brief Explanation of Pseudocode
Unary Expression Evaluation Process
Evaluate Unary Expression:
Let
valbe the result of evaluating UnaryExpression.This step involves evaluating the expression provided in UnaryExpression and storing the result in the variable
val.
Check if
valis a Reference:In JavaScript, a reference is a value that points to a memory location where the actual value is stored. If the reference cannot be resolved (i.e., the variable is not defined), it returns "undefined".
Example: If UnaryExpression is a variable name that hasn't been declared,
valwould be a reference that cannot be resolved.
Get the Actual Value of
val:This step retrieves the actual value from the reference or from the evaluated expression.
Example: If UnaryExpression is "true",
valwould be true.
Check for Undefined Value:
If the value of
valis undefined, the function returns "undefined".Example: If UnaryExpression is "undefined",
valwould be undefined.
Check for Null Value:
In JavaScript, null is an object that represents the absence of any value.
Example: If UnaryExpression is "null",
valwould be null.
Check for String Value:
If the value of
valis a string, the function returns "string".Example: If UnaryExpression is "'hello'",
valwould be "hello".
Check for Symbol Value:
Symbols are a new primitive type introduced in ECMAScript 2015.
Example: If UnaryExpression is "Symbol('example')",
valwould be a symbol.
Check for Boolean Value:
If the value of
valis a boolean, the function returns "boolean".Example: If UnaryExpression is "true",
valwould be true.
Check for Number Value:
If the value of
valis a number, the function returns "number".Example: If UnaryExpression is "42",
valwould be 42.
Check for BigInt Value:
BigInt is a built-in object that provides a way to represent whole numbers larger than 2(power 53) - 1.
Example: If UnaryExpression is "BigInt(9007199254740991)",
valwould be a BigInt.
Check for Function Object:
If the value of
valis an object and it can be invoked as a function, the function returns "function".Example: If UnaryExpression is "function() { return 42; }",
valwould be a function.
Return "object" Otherwise:
- If none of the above conditions match, the function returns "object".
I hope you learn from this article. See you next time 🙂